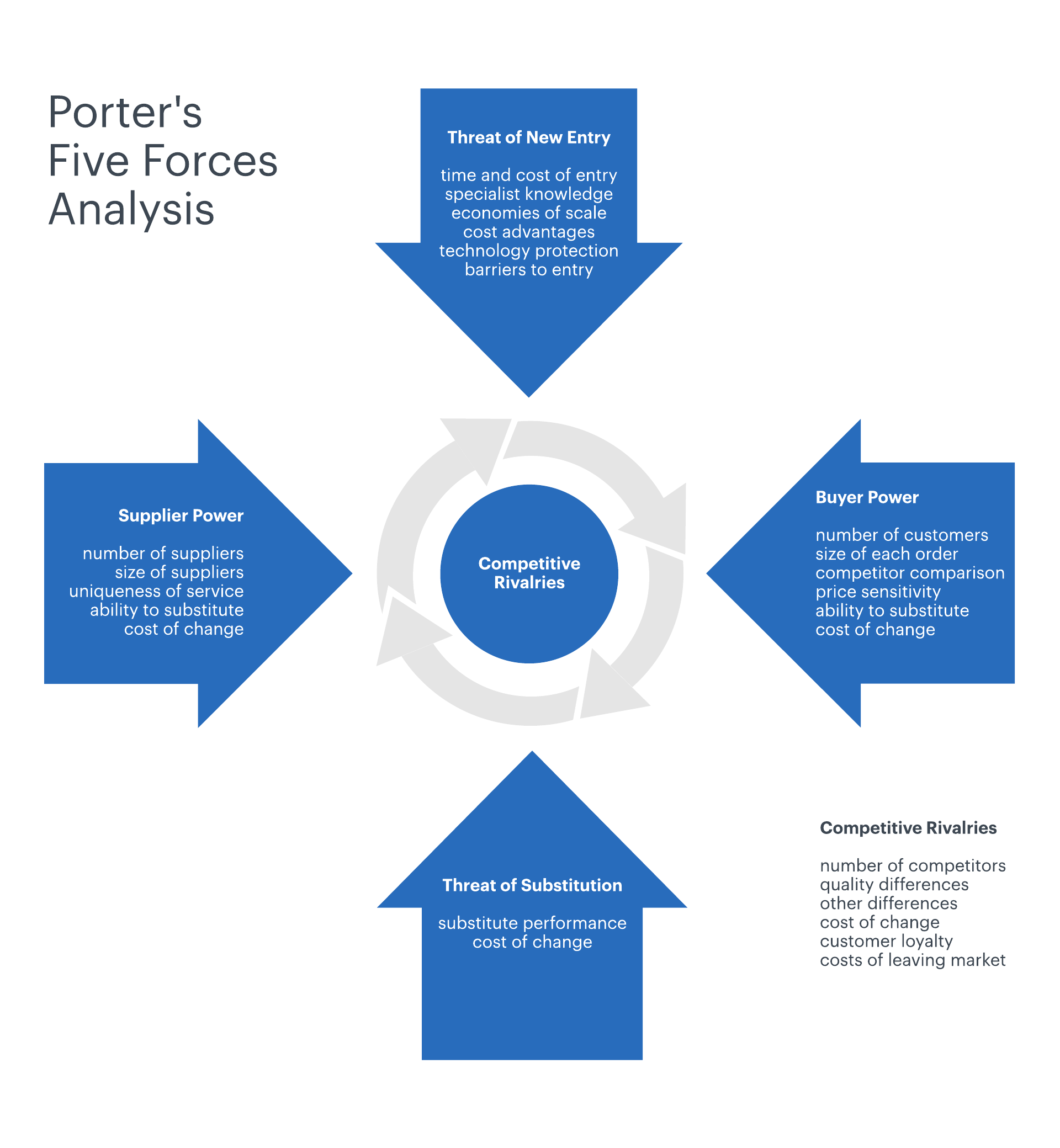
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
A model was put forward by Michael. E. Porter in an article in the Harvard Business Review in 1979. This model, known as Porter's Five Forces Model is a strategic management tool that helps determine the competitive landscape of an industry. Each of the five forces mentioned in the model and their strengths help strategic planners understand the inherent profit potential within an industry. The strengths of these forces vary across the industry to industry, which means that every industry is different regarding the profitability and attractiveness. The structure of an industry, even though it is stable, can change over time. These Porter’s five forces are as follows:
- Threat of New Entrants
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- Threat of Substitute Products or Services
- Rivalry Among Existing Firms
The Porter’s Five Forces model can be used to analyse the industry in which Apple Inc operates, in terms of attractiveness through inherent profit potential. The information analysed using the model can be used by strategic planners for Apple Inc to make strategic decisions.
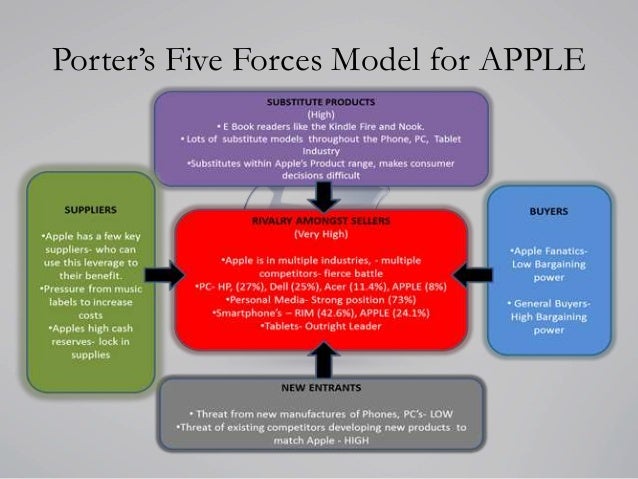
Because of five forces analysis, company addresses the bargaining power of buyers and competition that plays significant role in business. The five forces analysis also determines the fact that Apple Inc should focus on these external factors in order to be a market leader. Here is the Porter’s five force analysis of Apple. Analysis of Apple Inc According to Porter's Five Forces. 1426 Words6 Pages. The Apple Company According to Porter's Five Forces Introduction: Apple, Inc. Is widely recognized as one of the most innovative technology firms in the world. It owes much of this reputation to the identity of its leadership, and particularly to the sweeping changes wrought by the re-emergence of company co-founder Steve Jobs. Based on Porter’s five analysis, a number of factors may impact on the Apple Inc., profitability. One of the external forces that may affect profitability of the industry is the increased level of competition and rivalry. This will push the company profitability low as the firm adopts strategies to attract more customers. Analysis of industry competition Competition in a given industry is defined by the Micheal Porter’s five competitive forces shown in figure 3. This model can help to evaluate the impact on Apple and its ability to compete in market.
Apple Inc Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
This section analyses Apple Inc using each of the five forces of Porter’s model.
Threat of New Entrants
- The economies of scale is fairly difficult to achieve in the industry in which Apple Inc operates. This makes it easier for those producing large capacitates to have a cost advantage. It also makes production costlier for new entrants. This makes the threats of new entrants a weaker force.
- The product differentiation is strong within the industry, where firms in the industry sell differentiated products rather a standardised product. Customers also look for differentiated products. There is a strong emphasis on advertising and customer services as well. All of these factors make the threat of new entrants a weak force within this industry.
- The capital requirements within the industry are high, therefore, making it difficult for new entrants to set up businesses as high expenditures need to be incurred. Capital expenditure is also high because of high Research and Development costs. All of these factors make the threat of new entrants a weaker force within this industry.
- The access to distribution networks is easy for new entrants, which can easily set up their distribution channels and come into the business. With only a few retail outlets selling the product type, it is easy for any new entrant to get its product on the shelves. All of these factors make the threat of new entrants a strong force within this industry.
- The government policies within the industry require strict licensing and legal requirements to be fulfilled before a company can start selling. This makes it difficult for new entrants to join the industry, therefore, making the threat of new entrants a weak force.
How Apple Inc can tackle the Threat of New Entrants?

- Apple Inc can take advantage of the economies of scale it has within the industry, fighting off new entrants through its cost advantage.
- Apple Inc can focus on innovation to differentiate its products from that of new entrants. It can spend on marketing to build strong brand identification. This will help it retain its customers rather than losing them to new entrants.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- The number of suppliers in the industry in which Apple Inc operates is a lot compared to the buyers. This means that the suppliers have less control over prices and this makes the bargaining power of suppliers a weak force.
- The product that these suppliers provide are fairly standardised, less differentiated and have low switching costs. This makes it easier for buyers like Apple Inc to switch suppliers. This makes the bargaining power of suppliers a weaker force.
- The suppliers do not contend with other products within this industry. This means that there are no other substitutes for the product other than the ones that the suppliers provide. This makes the bargaining power of suppliers a stronger force within the industry.
- The suppliers do not provide a credible threat for forward integration into the industry in which Apple Inc operates. This makes the bargaining power of suppliers a weaker force within the industry.
- The industry in which Apple Inc operates is an important customer for its suppliers. This means that the industry’s profits are closely tied to that of the suppliers. These suppliers, therefore, have to provide reasonable pricing. This makes the bargaining power of suppliers a weaker force within the industry.
How Apple Inc can tackle the Bargaining Power of Suppliers?
- Apple Inc can purchase raw materials from its suppliers at a low cost. If the costs or products are not suitable for Apple Inc, it can then switch its suppliers because switching costs are low.
- It can have multiple suppliers within its supply chain. For example, Apple Inc can have different suppliers for its different geographic locations. This way it can ensure efficiency within its supply chain.
- As the industry is an important customer for its suppliers, Apple Inc can benefit from developing close relationships with its suppliers where both of them benefit.
Bargaining Power of Buyers

- The number of suppliers in the industry in which Apple Inc operates is a lot more than the number of firms producing the products. This means that the buyers have a few firms to choose from, and therefore, do not have much control over prices. This makes the bargaining power of buyers a weaker force within the industry.
- The product differentiation within the industry is high, which means that the buyers are not able to find alternative firms producing a particular product. This difficulty in switching makes the bargaining power of buyers a weaker force within the industry.
- The income of the buyers within the industry is low. This means that there is pressure to purchase at low prices, making the buyers more price sensitive. This makes the buying power of buyers a weaker force within the industry.
- The quality of the products is important to the buyers, and these buyers make frequent purchases. This means that the buyers in the industry are less price sensitive. This makes the bargaining power of buyers a weaker force within the industry.
- There is no significant threat to the buyers to integrate backwards. This makes the bargaining threat of buyers a weaker force within the industry.
How Apple Inc can tackle the Bargaining Power of Buyers?
- Apple Inc can focus on innovation and differentiation to attract more buyers. Product differentiation and quality of products are important to buyers within the industry, and Apple Inc can attract a large number of customers by focusing on these.
- Apple Inc needs to build a large customer base, as the bargaining power of buyers is weak. It can do this through marketing efforts aimed at building brand loyalty.
- Apple Inc can take advantage of its economies of scale to develop a cost advantage and sell at low prices to the low-income buyers of the industry. This way it will be able to attract a large number of buyers.
Threat of Substitute Products or Services
- There are very few substitutes available for the products that are produced in the industry in which Apple Inc operates. The very few substitutes that are available are also produced by low profit earning industries. This means that there is no ceiling on the maximum profit that firms can earn in the industry in which Apple Inc operates. All of these factors make the threat of substitute products a weaker force within the industry.
- The very few substitutes available are of high quality but are way more expensive. Comparatively, firms producing within the industry in which Apple Inc operates sell at a lower price than substitutes, with adequate quality. This means that buyers are less likely to switch to substitute products. This means that the threat of substitute products is weak within the industry.
How Apple Inc can tackle the Threat of Substitute Products?
- Apple Inc can focus on providing greater quality in its products. As a result, buyers would choose its products, which provide greater quality at a lower price as compared to substitute products that provide greater quality but at a higher price.
- Apple Inc can focus on differentiating its products. This will ensure that buyers see its products as unique and do not shift easily to substitute products that do not provide these unique benefits. It can provide such unique benefits to its customers by better understanding their needs through market research, and providing what the customer wants.
Rivalry Among Existing Firms
- The number of competitors in the industry in which Apple Inc operates are very few. Most of these are also large in size. This means that firms in the industry will not make moves without being unnoticed. This makes the rivalry among existing firms a weaker force within the industry.
- The very few competitors have a large market share. This means that these will engage in competitive actions to gain position and become market leaders. This makes the rivalry among existing firms a stronger force within the industry.
- The industry in which Apple Inc is growing every year and is expected to continue to do this for a few years ahead. A positive Industry growth means that competitors are less likely to engage in completive actions because they do not need to capture market share from each other. This makes the rivalry among existing firms a weaker force within the industry.
- The fixed costs are high within the industry in which Apple Inc operates. This makes the companies within the industry to push to full capacity. This also means these companies to reduce their prices when demand slackens. This makes the rivalry among existing firms a stronger force within the industry.
- The products produced within the industry in which Apple Inc operates are highly differentiated. As a result, it is difficult for competing firms to win the customers of each other because of each of their products in unique. This makes the rivalry among existing firms a weaker force within the industry.
- The production of products within the industry requires an increase in capacity by large increments. This makes the industry prone to disruptions in the supply-demand balance, often leading to overproduction. Overproduction means that companies have to cut down prices to ensure that its products sell. This makes the rivalry among existing firms a stronger force within the industry.
- The exit barriers within the industry are particularly high due to high investment required in capital and assets to operate. The exit barriers are also high due to government regulations and restrictions. This makes firms within the industry reluctant to leave the business, and these continue to produce even at low profits. This makes the rivalry among existing firms a stronger force within the industry.
- The strategies of the firms within the industry are diverse, which means they are unique to each other in terms of strategy. This results in them running head-on into each other regarding strategy. This makes the rivalry among existing firms a strong force within the industry.
How Apple Inc can tackle the Rivalry Among Existing Firms?
- Apple Inc needs to focus on differentiating its products so that the actions of competitors will have less effect on its customers that seek its unique products.
- As the industry is growing, Apple Inc can focus on new customers rather than winning the ones from existing companies.
- Apple Inc can conduct market research to understand the supply-demand situation within the industry and prevent overproduction.
Implications of Porter Five Forces on Apple Inc
By using the information in Apple Inc five forces analysis, strategic planners will be able to understand how different factors under each of the five forces affect the profitability of the industry. A stronger force means lower profitability, and a weaker force means greater profitability. Based on this a judgement of the industry's profitability can be made and used in strategic planning.
Apple Inc. The Company
Having started the journey in 1976 the company has seen many milestones. Today it appears that Apple Computer Inc. is the sole successful escapee from the IBM and Microsoft hegemony in the personal computer field. Headquartered in Cupertino, California, Apple Computer designs, manufactures and markets personal computers and related software, services, peripherals, and networking solutions. But today the company is better known for the iPods and iPhones. The IPod touch being the latest craze. Apple designs, develops, and markets portable digital music players along with related accessories and services, including the online distribution of third-party music, audio books, music videos, short films, and television shows. John Sculley, previously the CEO joined Apple in 1985. Sculley had the valuable experience of the ‘Cola-War’ between Coke and Pepsi. He was full of marketing ideas and wanted to implement them in Apple as well. Steven Jobs, more of technology oriented initially found this approach little weird, but later gave Sculley a free hand (Yoffie and Slind, 2007). Sculley was later replaced with Michael Spindler in 1993 who lasted only three years, making way for Gil Amelio, who came out with the Macintosh product range for designers and artists. From here onward Apple brought out radical changes in the marketing strategies as well. Amelio also realized that the ‘free for all’ culture where anybody was free to defy anybody in the company, is causing losses to the company. He believed in more conventional strategy where project managers are supposed to sincerely implement the strategies devised by the strategists, whatever the outcome.
The Business Model
Haven’t found the relevant content?Hire a subject expert to help you with Apple Inc. analysis
$35.80 for a 2-page paper
Hire verified expertThe company primarily operates in the Americas, Europe and Japan. It employs about 14,800 people. Apple experienced good success during the late 1980s but equally testing times during the 90s. Realizing the importance of strategic alliance, Apple also had a tie up with IBM in 1991 to target the areas where Apple lacked the developmental skills but owing to cultural and other differences the alliance did not last long. The 21st century seems to be progressing well so far for the company and proving to be particularly success oriented for Apple with its range of iPods and iTunes being very much popular amongst the young music lover fans. By the end of year 2000 Apple was able to sell some 2 million iPods leading to a 30% share of digital music players. Though the profit margin is miniscule as Apple has adopted the penetrative pricing strategy for its iPods, yet Apple is determined not to loose the initiative this time to its competitors like Sony, Phillips, Samsung etc. Year 2004 also saw the launch of a new 20 GB digital walkman from Sony, but so far iPods has been proving to be music to the ears of Apple.
Value Chain of Apple
While planning for long term objectives, the company will have to remain competitive. Porter’s value chain provides an important tool for a tool for developing and sustaining competitive advantage for a company. It underlines the need for creating and retailing value for the organisation. Value, in general, can be defined in respect of customers, employees and owners or other stakeholders. Value addition is considered an important ingredient in dealing with the competitions, as it provides the organisation with a strategic tool. An individual’s beliefs or conceptions about what is desirable, good or bad – forms the value system (Kotler, 1974). The term “value” can be defined in different ways according to the adopted perspective of the analysis: it is possible to determine a “customer value”, a “firm value”, a “stakeholder value” (Mele and Colurci, 2006).
Also read about Apple differentiation strategy
For the companies to identify their sustainable competitive advantage, Michael Porter developed a generic value chain with inter-related activities which are common in many firms. Porter identifies primary and support activities. Primary activities are the ones which generate a profit margin by adding value. These activities can be instrumental in providing a sustainable competitive advantage for the organisation either collectively or individually. Porter’s value chain framework (1985) in general is accepted as the language for representing as well as analyzing the logic of firm-level value creation. The customer will prefer to deal with the company which values its association with the customer. This will help in retaining the customer base. And loyal customers happen to be good brand ambassadors for a company/ product, which will ultimately help the company in sustaining its competitive advantage.
For a customer, value proposition include, Access to products, need fulfillment, desire fulfillment, increased choice, new consumption patterns, Problem solving features, and interactivity. In the value chain, value is created in the goods or services through efficient production of goods and services based on a variety of resources. The company is considered as a series or chain of activities. Primary activities in the value chain of Apple include;
§ Inbound logistics: These include the raw material supplies, knowledge sources, consultancies, supplier management etc. Key suppliers of Apple include IBM and freescale.
§ Production: After planning out the strategies, the inbound logistics are put in use to give out a finished product or a full-fledged service component.
§ Outbound logistics: Outbound logistics include taking care of distribution network, inspecting the quality of finished goods and services, planning out marketing and sales strategies etc.
§ Marketing and sales: Marketing and sales forms an important component of the value chain as it is the main interface between the company and the customer.
§ Service: Once the product or service is delivered to the customer, then comes taking a feedback from the customer. This has become very important in order to establish the company’s brand equity and customer’s loyalty. Futuristic needs are also projected by way of accepting regular inputs from the customer.
Porter’s five forces analysis
In case of Apple Inc the Five Competitive Forces can be typically described as follows:
i. Bargaining Power of Suppliers: 'Suppliers' comprises all sources for inputs that are needed in order to provide goods or services.
a. Apple is dependent on IBM for its supply of the PowerPC G5 processor which is used in its current Power Mac, Xserve, and iMac G5 products. The company is therefore susceptible to a supply risk for key components from its supplier who also happens to be a competitor. In the past IBM has experienced manufacturing problems with the PowerPC G5 processor, which resulted in delaying the shipment of various products and constrained certain product shipments during the second half of 2004 and the first quarter of 2005.
b. Freescale is the sole supplier of the G4 processor, which is used in the company’s eMac, Mac mini, and portable products.
In a market where speed to market is extremely vital for beating the competition, Apple’s dependency for such key components on its long time rival companies could result in its being at a competitive disadvantage. In fact IBM has made at least two unsuccessful attempts in the past to take over Apple Inc.
ii. Bargaining Power of Customers: Customers of course have plenty of options in the market place. And the customer will weigh all his options before going in for the purchase. Therefore Apple needs to be innovative and rely more on product differentiation. Sony, Phillips, and Samsung threaten to take away its monopoly over the iPod with their own version of walkman and minidisks.
iii. Threat of New Entrants: Though it is not easy for new entrant to enter the PC and Software industry as it is a capital intensive business as the economies of scale (minimum size requirements for profitable operations) leaves little room for a new start up company challenging the existing market share, yet the threat emanates from the existing competitors. If Microsoft decides to jump into the music store software, then it could be create an uncomfortable position for Apple, as Microsoft is known for aggressive an penetrative marketing.
iv. Threat of Substitutes: Threat from substitutes exists if there are alternative products with lower prices and with better performance parameters for the same purpose. Apple faces aggressive competition in all areas of its business. The market design, manufacture, and sale of PCs and related software and peripheral products has become highly competitive. Moreover this market continues to be characterized by rapid technological advances in both hardware and software development, which results increasing the capabilities of existing products and software. This is resulting is the frequent introduction of new products with much reduced prices and better feature, and performance. Apple needs to keep its R&D activities in motion all the time.
v. Competitive Rivalry between Existing Players: Though to certain extent Apple has been able to lower the competitive rivalry between itself and Microsoft by way of a strategic tie-up, but growth in business is one of the objectives of both the companies. Therefore Apple has a big task in hand. IBM also happens to be a supplier for Apple, but it must be remembered that IBM is a rival as well.
Apple’s Core Competency
The core competency of apple is determined with its ‘making the technology easy to use’. PC and software development are the two areas the company stands tall amongst the rest. Many times it has come in direct conflict with the other big name in the industry, Microsoft, but that is part of the business rivalry and both companies seem to take that into their stride while marching ahead, writing success stories. For that very reason the new Apple iPhone has been works perfectly fine with windows and other related features. iPhone is the latest addition in the digital communicationfamily for a phone, music player, video player, internet device, and camera all in one.
References:
Apple (2007). Available online at http://www.apple.com/
Kotler, Philip (1974), Marketing Management, 2nd Ed., Prentice Hall, NY.
Mele, Cristina and Colurci, Maria (2006), ‘The evolving path of TQM: towards business excellence and stakeholder value’, International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management Volume 23 Number 5
Porter, M. (1985). Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. Free Press, New York.
Yoffie, David B. and Slind, Michael (2007). Apple Computer-2006. Harvard Business School, May 30, 2007.
Haven’t found the relevant content?Hire a subject expert to help you with Apple Inc. analysis
Five Forces Analysis Apple Inc. Free
$35.80 for a 2-page paper
Five Forces Analysis Apple Inc
Hire verified expertCite this page
Apple Inc. analysis. (2018, Nov 20). Retrieved from https://phdessay.com/apple-inc-analysis/